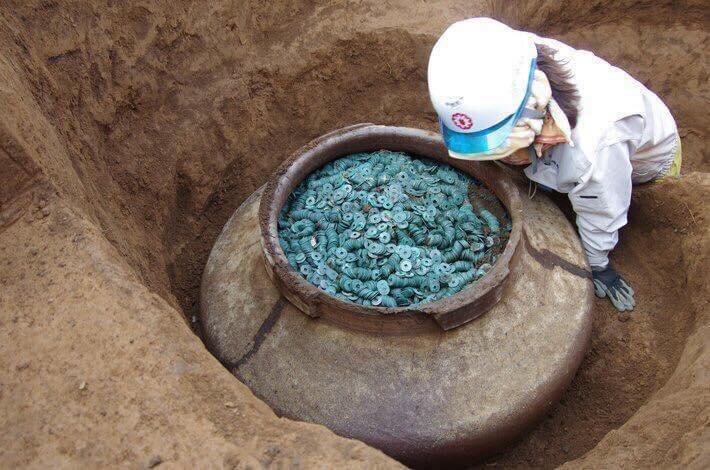
In a town just north of Tokyo, a ceramic jar filled with thousands of bronze coins has been unearthed at the site of a fifteenth-century samurai’s residence in 2018
(Courtesy Saitama Cultural Deposits Research Corporation)
According to archaeologist Yoshiyuki Takise of the Saitama Cultural Deposits Research Corporation, the coins, which were cast in China, may have been an offering to the deity of the earth, or may simply have been buried for safekeeping.
Markings on a wooden tablet found on the rim of the jar indicate it could contain as many as 260,000 coins, a number that Takise says far exceeds what one would expect to find in circulation in what was then a rural area.
Ohara-tei (Site of Old Samurai Residence)
Samurai (侍) were the hereditary military nobility and officer caste of medieval and early-modern Japan from the 12th century to their abolition in the 1870s. They were the well-paid retainers of the daimyo (the great feudal landholders). They had high prestige and special privileges such as wearing two swords. They cultivated the bushido codes of martial virtues, indifference to pain, and unflinching loyalty, engaging in many local battles. During the peaceful Edo era (1603 to 1868) they became the stewards and chamberlains of the daimyo estates, gaining managerial experience and education. In the 1870s samurai families comprised 5% of the population. The Meiji Revolution ended their feudal roles, and they moved into professional and entrepreneurial roles. Their memory and weaponry remain prominent in Japanese popular culture.
By ERIC A. POWELL
Left to right: ceramic jar, jar with coins, and wooden tablet. (Courtesy Saitama Cultural Deposits Research Corporation)