In the following video we will be listening to ancient Egyptian music. This is some calming, relaxing, music which we hope helps your day be a little lighter. It can help you study, read or you can simply listen. May peace and calm be always by your side!
Archaeologists Just Discovered What No One Was Supposed To See
From ancient Egyptian tombs to Bronze Age burials, these finds give us a unique glimpse into the lives and loves of our ancestors. Whether they were high-ranking officials or common folk, these couples demonstrate the enduring nature of love and the importance of relationships in the past.
In this video, we'll be exploring some of the most interesting and poignant discoveries of ancient couples that have been made over the years.
'Römerwein': An extremely rare bottle of wine, 1,650-years-old
For a few years now, contemporary historians have been debating the future of the oldest bottle of wine in the world, known as the Speyer wine bottle, or “Römerwein.”
Historians have split opinions on whether the bottle should be opened or not.
This extremely rare artifact is 1,650-years-old and it is placed in the Historical Museum of the Palatinate in Germany.
The glass amphora has handles in the shape of dolphins and is sealed with wax. The contents of the bottle is about one-third olive oil which in the past was used as a preservative that prevented the wine from oxidizing.
The Speyer bottle was found in the grave of a Roman nobleman in 1867, in the Rhineland-Palatine region of Germany and caused a real stir among historians and archaeologists at the time.
It’s been said that the noble owner, believed to be a high ranking Legionnaire, was buried with the bottle of wine, an ancient custom which represents the Romans’ beliefs in the after-life, that is, sending valuable objects with the body of the deceased so she or he can use them in the “hereafter.”
Reportedly, the tomb near the city of Speyer also contained the sarcophagi of his two spouses.
The antique bottle, which represents thousands of years of human history and customs, was named after the city of Speyer. In the glory days of Ancient Rome, wine and wine cults were diligently observed.
One of the inventions of Hero of Alexandria, an engineer who was centuries ahead of his time, was a delightful party centerpiece that seemingly turned one liquid into another.
His trick jug incorporated two separate, sealed compartments and some clever pneumatics to make it seem that water added to the vessel was dispensed as wine. This is one of several similar devices that Hero describes in his Pneumatica.
During WWI, a chemist analyzed the Speyer bottle but never opened it so the wine was given to the Historical Museum of the Palatinate collection in Speyer. Over time, numerous scientists have hoped to obtain permission to analyze the bottle’s contents thoroughly, though nobody has been granted one yet.
Some scientists and microbiologists are adamant that the bottle shouldn’t be opened, among them Ludger Tekampe, the curator of the Folklore Wine Museum collection. “We are not sure whether or not it could stand the shock to the air. It is still liquid and there are some who believe it should be subjected to new scientific analysis but we are not sure.” said Tekampe on the matter.
This rare artifact of the ancient world was created during the early days of the tradition of wine production and consumption, which was begun by the ancient Greeks. The tradition was later embraced by the ancient Romans, who also took Dionysus, the Greek god of agriculture, wine, and fertility, and renamed him Bacchus.
Contrary to the general notion and belief that the older the wine is, the better, the Speyer wine is presumed to be undrinkable. According to the Daily Mail, Professor Monika Christmann said that although the Speyer wine might not be microbiologically spoiled, it “would not bring joy to the palate.”
Biggest Unsolved Mysteries In The World!
Check out the Biggest UNSOLVED Mysteries In The World! From lost treasures like the ark of the covenant to other strange unexplained mysteries, this top 10 list of bizarre and still unsolved cases is very intriguing!
Most Mysterious Ancient Structures In The World!
Check out the Most MYSTERIOUS Ancient Structures In The World! From unexplained ancient architecture to mysterious hidden buildings, this top 10 list of mysterious ancient ruins has some of the most bizarre discoveries!
What Happened To Atlantis?
Check out what happened to atlantis! This top 10 list shows the most current theories surrounding the location of the mysterious los city of atlantis!
Amazing Discoveries That Prove Giants Actually Existed!
Check out these amazing discoveries that prove giants actually existed! From real giant skeletons to other mysterious and unexplained discoveries, this top 10 list show some of the biggest discoveries in history!
Most Terrifying Creatures From Greek Mythology!
Check out the Most TERRIFYING Creatures From Greek Mythology! From legendary monsters to mysterious beasts, this top 10 list of mythical creatures from ancient greece will amaze you!
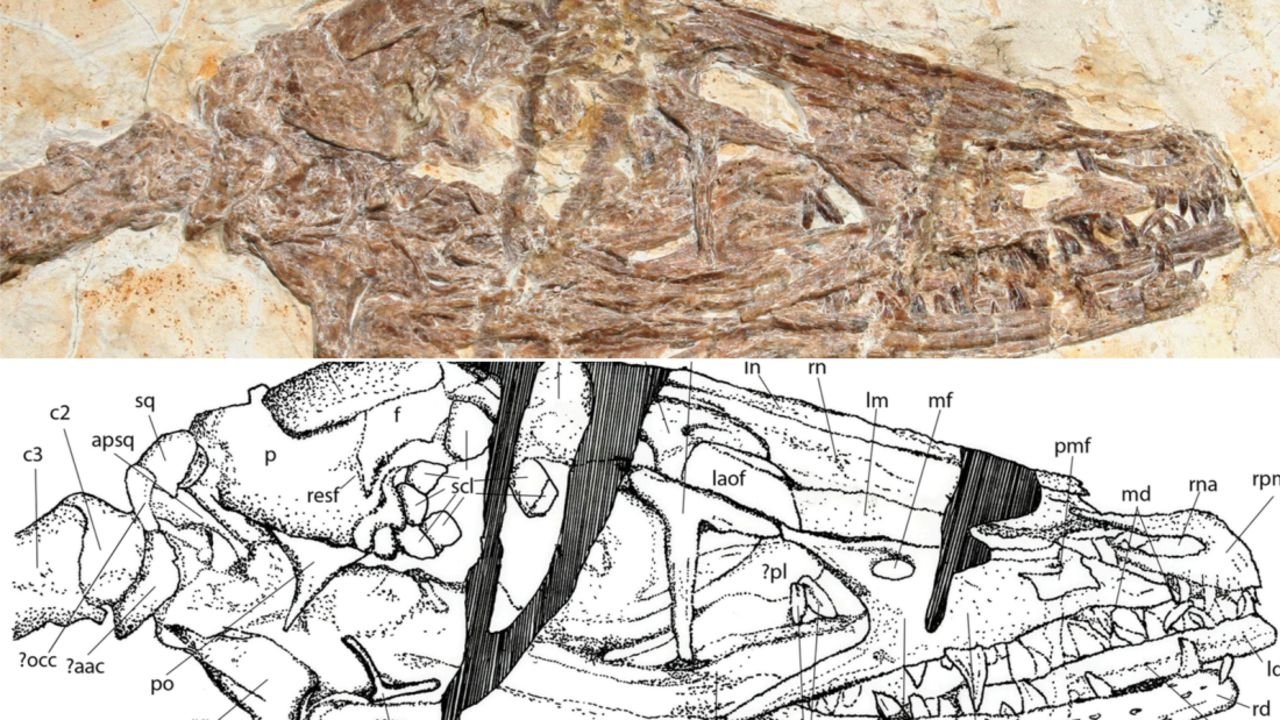
120 million-year-old ‘dancing dragon’ fossil found in China
About 120 million years ago, a “dancing dragon” lived in China’s Jehol Province. The discovery of a fossil belonging to the small feathered dinosaur is new to science and helps bridge the gap between dinosaurs and birds.
Researchers named the dinosaur Wulong bohaiensis, which translates to “a dancing dragon.”
The dinosaur was about the size of a raven but double its length with a long, bony tail. Its entire body was covered with feathers, complete with two plumes at the tail’s end.
Despite its small size, it had a fierce, narrow face and a mouth full of sharp teeth. Like a bird, it had small, light bones and wing-like forelimbs. And there were also a number of feathers on its legs.
The fossil was initially discovered in the fossil-filled Jehol Province a decade ago by a farmer and was placed in China’s Dalian Natural History Museum.
Researchers, including Ashley Poust, a postdoctoral researcher at the San Diego Natural History Museum, later analyzed the fossil (at the time, Poust was still a student at Montana State University).
The findings were published last week in the journal The Anatomical Record.
“The new dinosaur fits in with an incredible [range] of feathered, winged animals that are closely related to the origin of birds,” Poust, the study’s author, said. “Studying specimens like this not only shows us the sometimes surprising paths that ancient life has taken, but also allows us to test ideas about how important bird characteristics, including flight, arose in the distant past.”
This dinosaur was a juvenile when it died, according to its bones, but its feathers resembled that of a mature adult. This suggests that the feathers grew quickly, unlike modern birds, which take time to grow their mature feathers.
“Either the young dinosaurs needed these tail feathers for some function we don’t know about, or they were growing their feathers really differently from most living birds,” Poust said.
The dinosaur was an early relative of Velociraptors, which lived 75 million years ago. Its contemporaries would have been Microraptors, small feathered dinosaurs that resembled birds.
The researchers actually sliced into several bones from the fossil and studied them with microscopes to understand the different regions of the skeleton. They also compared it to a close relative that also appeared more mature, known as the Sinornithosaurus.
Surprisingly, that dinosaur was also still growing when it died. The researchers said that histology, or cutting up the bones, was the only way for them to truly know the life stage of the dinosaurs when they died.
“We’re talking about animals that lived twice as long ago as T. rex, so it’s pretty amazing how well-preserved they are,” Poust said. “It’s really very exciting to see inside these animals for the first time.”
Fossils from the Jehol Province have painted a portrait of the diverse life that once flourished there. It’s an area in northeastern China full of exceptionally preserved fossil discoveries that has been studied for the past 90 years.
Researchers learned that birds, pterosaurs and bird-like dinosaurs all lived in the environment at the same time. This is also when flowering plants initially began to flourish.
“There was a lot of flying, gliding and flapping around these ancient lakes,” Poust said. “As we continue to discover more about the diversity of these small animals, it becomes interesting how they all might have fit into the ecosystem. It was an alien world, but with some of the earliest feathers and earliest flowers, it would have been a pretty one.”
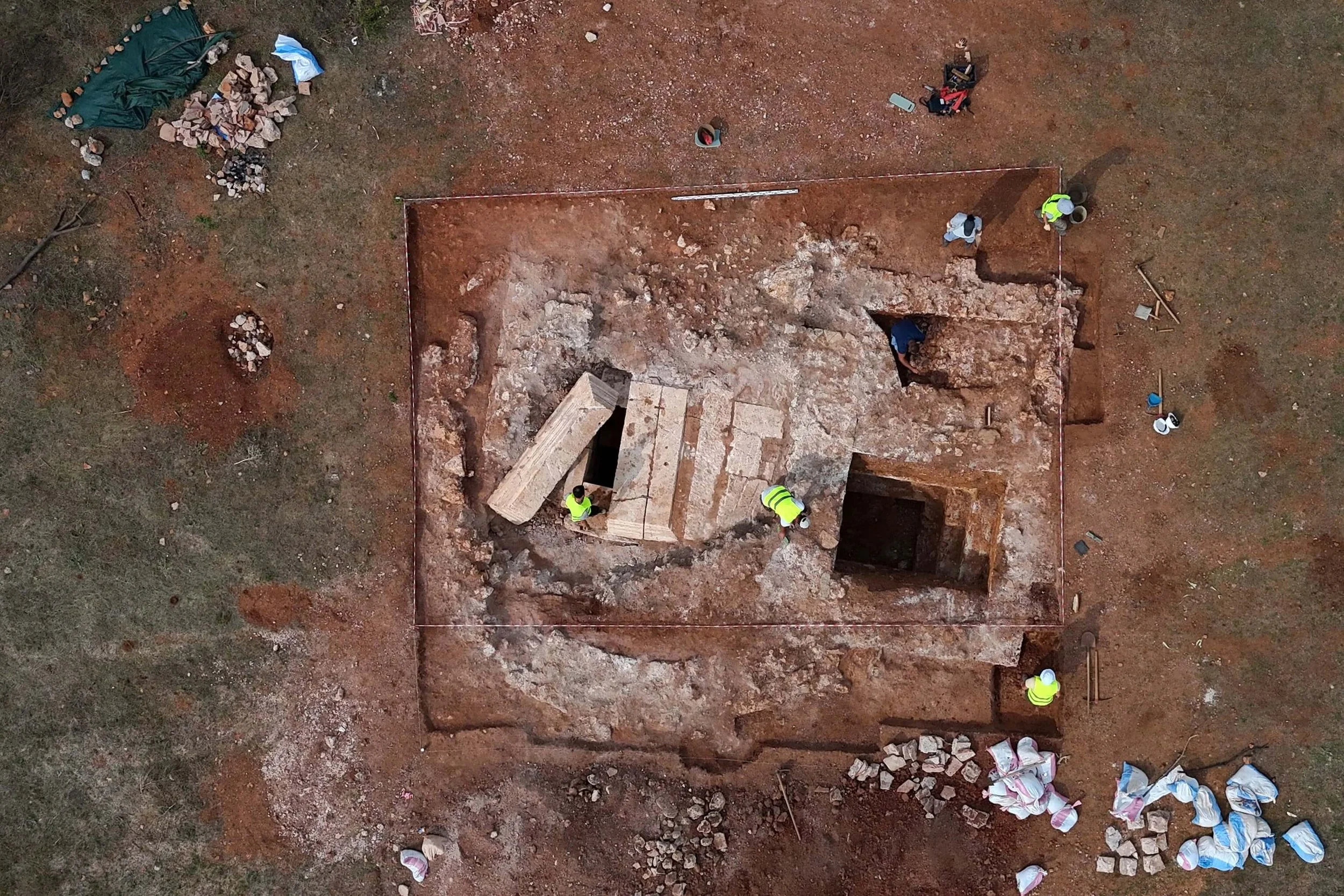
Inside the Tomb of the First Aztec Emperor
The Templo Mayor excavation in present-day Mexico City has unearthed an exciting site; in March 2019, archaeologists found a cache of sacrifices and offerings that may indicate the burial of royalty. The trove was discovered near the holiest temple in the Aztec world, Templo Mayor, which has been described in historical accounts as the resting place of the Aztec kings. Archaeologists have never found an Aztec royal burial despite decades of excavations, but this recent discovery may lead to the first.
Top 10 | Beautiful and Expensive Imperial Egg of Russia from the House of Faberge
In 2010, an American scrap-metal dealer visited an antique stall somewhere in the United States and purchased a golden egg sitting on a three-legged stand. The egg was adorned with diamonds and sapphires, and it opened to reveal a clock. Intending to sell the object to a buyer who would melt it down for its component metals, the dealer purchased this egg-clock for $13,302. He then had trouble selling it, as potential buyers deemed it overpriced.
The dealer had valued it incorrectly—but not the way he originally thought. In 2014, the man—who remains anonymous—discovered that his little golden objet d’art was one of the 50 exquisitely bespoke Fabergé Easter eggs created for imperial Russia’s royal Romanov family. Its value? An estimated $33 million.
The Romanovs’ extravagant royal Easter egg tradition began with Czar Alexander III in 1885. Alexander was then in the fifth year of his reign, having succeeded his father, Alexander II, who had been killed by bomb-wielding assassins. In 1885, Alexander sought an Easter gift to surprise and delight his wife Maria Feodorovna, who had spent her early years as a Danish princess before leaving Copenhagen to marry him and become a Russian empress. He turned to Peter Carl Fabergé, a master goldsmith who had taken over his father’s House of Fabergé jewelry business in 1882.
Geneticists Have Found Traces Of Biblical Figures Hidden In The DNA Of Modern Populations
An international team of genetic experts examine the ancient DNA extracted from 93 individuals. All these people died over a period of 1,500 years at five different sites in the Middle East. All of them were part of the Canaanite civilization which thrived for some 4,700 years up until around 1200 B.C. However, what surprises the scientists is the link they can now make between these ancient Biblical people and their modern-day descendants.
When Experts Dug Beneath Jerusalem’s Holy Western Wall, They Found These Eerie Underground Chambers
Archeologists are working at an Israel Antiquities Authority archeological dig beneath Jerusalem’s iconic Western Wall and the adjoining plaza. They’re delving under a mosaic floor that was once part of a Byzantine building dating back 14 centuries. And what they find underground astonishes both them and the experts running the excavation.
Archaeologists discover massive underground city under Grand Canyon [Mystery]
Mr. Kinkaid, a Smithsonian Institute archaeologist in the early 1900s, went on to discover the Western States. His journey took him to several locations, but one of them may have changed how we think about the Grand Canyon and government organizations studying history. They discovered a mysterious Egyptian city underneath the Grand Canyon!
The discovery consists of a mysterious network of vast caverns; surprisingly, they were brimming with weapons, statues, seeds, and other treasures. Also, there are rumors of Egyptian pyramids and relics in the forbidden area of the Grand Canyon!
Within the depth of the Grand Canyon, lives a huge mystery. According to recent reports, rocks dating back to one billion years' have suddenly vanished. Sounds unbelievable, right? But it has happened. The Great Unconformity was first described many years ago, and the news was so big that it completely shook the scientific community. None of them had ever seen anything like it before.
The natural question here arises: Where did the rocks go if they disappeared? Scientists and archaeologists kept thinking about the answer, but no one found any. However, a recent discovery has unveiled a giant city located underground right beneath the Grand Canyon. So, is it related to the mystery, and if yes, then how?
Secret Tomb Of Cleopatra Finally Found!
Experts have been searching for Cleopatra's tomb for decades. Archaeologists continue searching for the mausoleum of the last Queen of Egypt, and there are several theories about where she was buried. Egyptologists and archaeologists have scoured the land of Egypt but have yet to find the tomb of Queen Cleopatra.
In this video, we will explain where Cleopatra, the last Pharaoh of the Egyptian dynasty, is said to have been buried. So if you have ever wondered Who is Cleopatra? Why is Cleopatra's tomb so elusive, and why are archaeologists so desperate to find it? Sit back and enjoy.
The valley of Kings
For thousands of years, many features of ancient Egypt remained a mystery. One of them is a secret tomb that a later dynasty Pharaoh commissioned and built in the Valley of the Kings to preserve the bones of his ancestors. Let's quickly learn about these tombs.
The Valley of the Kings, home to the royal tombs of several kings and queens, was not as heavily guarded during Egypt's decline in power; therefore, the thieves made several raids on the tombs. The damaged and desecrated mummies of his 18th, 19th, and 20th Dynasty predecessors were reburied in a safe place by a post-21st Dynasty king. He secretly built a tomb and reburied the remains of his ancestors.
Discovery a cave-dwelling human and snake hybrid creature in Greek Mythology is Echidna – Mother of monsters
In Graeco-Roman tradition, Echidna is a hybrid creature, a gigantic half-woman, and half snake. As a tall, full of charm, and beautiful woman from the waist below, she was a hideous serpent.
In other words – Echidna - described by Hesiod as an 'impossible monster' - is a remarkable creature and a mother of a pantheon of spirits with fierce temperament, who, among many other monstrous spirits, represented dark forces. These forces were created in the earliest times of the violent wars conducted by the gods. Some of these creatures survived the conflicts and continued to haunt and seriously endanger humans.
Echidna was an offspring of the primal gods Gaia and Tartarus (or Chrysaor and Callirhoe), Echidna never aged, but she was not immortal. She was a proud mother of many terrifying children with her brother and husband Typhoon. She represented the corruption of the earth, decay, and disease.
One of them was Hydra, and others like Cerberus (Kérberos), the two-headed hound Orthos, who guarded Geryon's cattle and was killed by Heracles, the goat/lion/serpent Chimera, the Nemean Lion, the Sphinx, and the Eagle that ate Prometheus's liver.
Yet another extraordinary and frightening child of hers was the Griffin Vulture, a monstrous bird from Graeco-Roman mythology, and most probably Ladon, the many-headed watchful, dragon-like serpent that guarded the Golden Apples of the Hesperides, the sacred garden.
According to Pindar (Pindarus), c. 518 - 438 BC, an ancient Greek lyric poet from Thebes, Echidna gnawed into the light from her mother's womb. She lived in a cavern close to the land of Scythia, and usually, she emerged, showing only her human parts to attract human males. Once she had captured her victims, she would quickly embrace them in her serpentine coils and consume them.
According to Herodotus, Greeks living in Pontus, a region on the southern coast of the Black Sea, told a story of an encounter between Heracles, the son of Zeus and a divine hero in Greek mythology, and this snaky female creature. Heracles drove the cattle of Geryones through the area that would later become Scythia. One morning he awoke and discovered that his horses had vanished. While searching for them, he "found a creature of double form in a cave that was half maiden and half serpent."
She had the horses and promised to return them if Heracles would have sex with her. Heracles agreed, and she had three sons with him: Agathyrsus, Gelonus, and Scythes. She asked Heracles what she should do with his sons: "shall I keep them here (since I am the queen of this country), or shall I send them away to you?"
Heracles gave her a bow and belt and told her that when the boys were grown, whichever would draw the bow and wear the belt keep him and banish the others. The youngest son, Scythes, fulfilled the requirements and became the founder of the Scythians.
Death Of Echidna
Many versions of the myths are associated with Echidna, known as the "mother of all monsters." One says Hercules, Bellerophon, or Oedipus killed her. According to another, she was strangled in her sleep by Argos Panoptes, a giant with a hundred (or three-hundred eyes) who was Hera's servant. The killing of the serpent-legged monster Echidna as she slept in her cave was believed to be Argos'great achievement for the Olympian pantheon.
According to another story, Echidna was immortal. Zeus left her on earth after the victory over the Titans so that she and her descendants could later challenge heroes, according to Hesiod ('he, who emits the voice'), an ancient Greek poet that flourished c. 700 BC.
Most myths and legends about Echidna do not focus on her but her famous and horrible monster children.
As told in the Iliad, the hero Bellerophon was ordered by the king of Lycia to kill the Chimera. The truth is the king wanted rather than the Chimera to kill Bellerophon, but the hero, who the gods miraculously protected, succeeded in killing Echidna's monster-child, Chimera, who Bellerophon shot with an arrow.
World’s Oldest Water lіeѕ At The bottom Of A Canadian Mine And Is 2 Billion Years Old
In 2016, deep down within a Canadian mine researchers made an ancient discovery: the world's oldest pool of water. At a depth of roughly 3 kilometers (1.8 miles), the water dates to an impressive 2 billion years old.
The discovery pushed back the date for the oldest known water by at least 500 million years. The previous record was held by water found in the same mine by the same team back in 2013, and came from a depth of around 2.5 kilometers. The mine is in fact the deepest basal metal mine in the world, as the search for copper, zinc, and silver is taking the miners deeper and deeper into the Earth’s crust.
When the miners dug deeper, the researchers took the opportunity to explore further into the mine. They analyzed the water discovered by studying the gases trapped inside. Gases like helium and xenon can get trapped in water stuck in rock cracks, and measuring these can tell how old the water is.
“When people think about this water they assume it must be some tiny amount of water trapped within the rock,” Professor Barbara Sherwood Lollar, who presented the discovery, told BBC News. “But in fact, it’s very much bubbling right up out at you. These things are flowing at rates of liters per minute – the volume of the water is much larger than anyone anticipated.”
What is more, the vast age of the water is not the only important discovery. When the researchers analyzed the liquid, they found traces of life within it. While they are yet to find actual living bacteria, what they did discover was, in effect, the fingerprint of life. From this, they are able to infer that there has been some form of microbiology living within the water and over a very long time period.
The fact that something has been able to survive, and indeed flourish, in water that is so old and so deep within the Earth has some important implications. Not only can it tell us about life on Earth billions of years ago, but it may also help in the search for life off-world. While rivers no longer flow on the surface of Mars, there are still pockets of water and ice under the surface. These are nowhere near as deep as the water discovered in Canada, and it is possible that these pockets could provide the conditions necessary for microorganisms to live.
Ancient Giant Trees Found Petrified in Thailand
Fossil trees that approached the heights of today’s tallest redwoods have been found in northern Thailand. The longest petrified log measures 72.2 meters (237 feet), which suggest the original tree towered to more than 100 meters (330 feet) in a wet tropical forest some 800,000 years ago.
The trees appear to have been closely related to a species alive today called Koompassia elegans, which belongs to the same family as beans, peas and black locust trees, explained lead author of the study, Marc Philippe of France’s University of Lyon. That is to say, the ancient trees are not closely related to today’s tallest trees, which are the Eucalyptus (gum trees) of Australia and Sequoia (redwoods) of California. Both of those living trees can reach about 130 meters (425 feet) in height.
Interestingly, there are no trees living today in Thailand that approach the size of the ancients.
“Highest trees nowadays in Thailand are almost 60 meters (200 feet),” wrote Philippe in response to my email query about his new paper coming out in the April issue of the journal Quaternary Science Reviews. ”To my knowledge the highest tree yet recorded in Thailand is a Krabak tree, belonging to the Dipterocarpaceae (‘tropical oaks’), 58 meters (190 feet) tall.”
The sediments in which the fossil trees were found suggest that they lived in a wet forest at the edge of a lowland plain. Today the fossil trees are at an elevation of 170 meters (550 feet) above sea level and the climate flips between wet and dry seasons — what’s called monsoonal. Philippe says it’s possible there has been some uplift of the region since the trees fell.
Just how these buried trees were found is an interesting story in itself. A small section of a large petrified log was found ten years ago by a villager in a reserve forest at Ban Tak District, Tak Province. The discovery was reported to officials of the National Park, Wildlife and Plant Conservation Department and so an official came out to examine the log and surveyed the surrounding area. The log was then excavated to a length of 21 meters (70 feet) without reaching the end. Ground penetrating radar was brought in and found that 30 meters (100 feet) of trunk were still unexposed. In 2005, funds were found to excavate the whole trunk. At present, seven of nine discovered petrified trunks have been excavated, mostly in 2005.
“The result was the appearance of what is considered the world’s longest piece of petrified wood, with a length of 72.22 meters” (236.9 feet), the researchers report. “In 2006, the name of the park was changed to the Petrified Forest Park because of the fascinating discoveries.”
As to why there were big trees in the past that are unrelated to today’s giant trees, it appears to be just another case of what’s called convergent evolution. That’s where similar environmental factors lead to traits that are similar in unrelated species. Think rheas (South America), ostriches (Africa) and emus (Australia). All are large, unrelated flightless birds that evolved on different continents. I’m not sure what drives trees to grow taller, but a dense forest and a competition for sunlight is part of it. It seems likely that over hundreds of millions of years that plants have been around there have been lots of very tall tree species, probably from every family of plant. It’s just an extremely very rare thing to get an entire petrified trunk to confirm it.
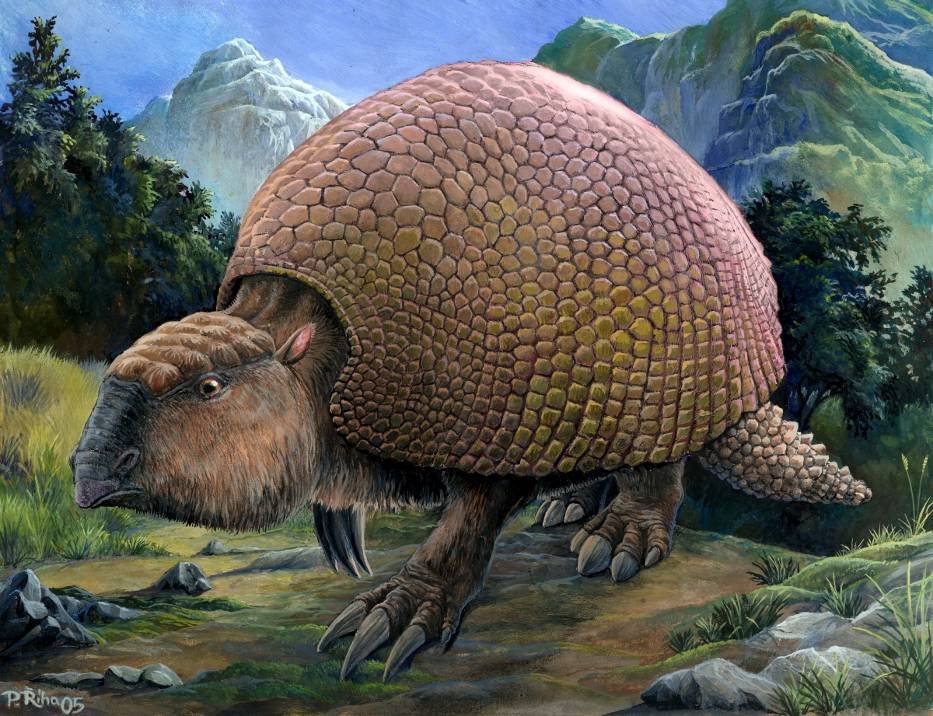
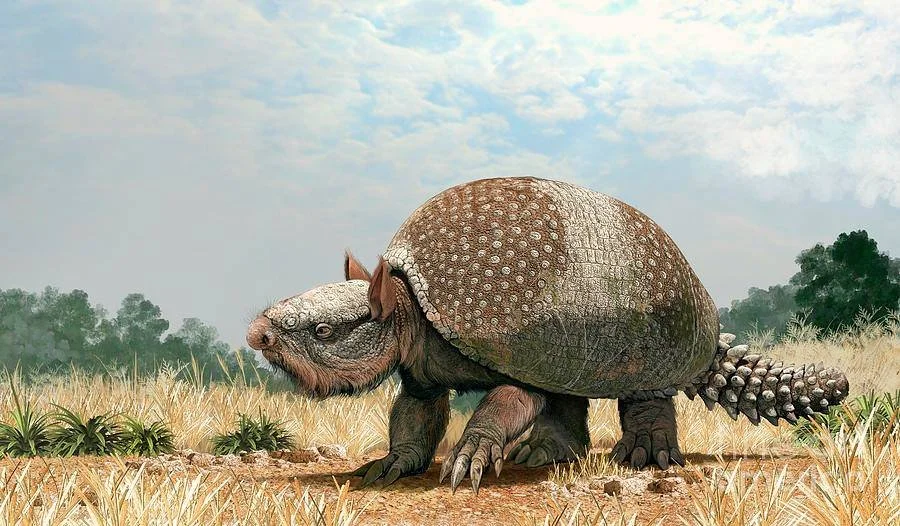
Discovered ѕkeleton of animal “Glyptodon” nicknamed “Walking foгtгeѕѕ”
An extraordinary discovery has been made by a farmer in Argentina who was fortunate enough to stumble across the fossil remains of four enormous Glyptodon fossils in the Vallimanca stream channel while transporting cattle. A post from the Institute of Archaeological and Palaeontological Investigations of the Pampa Quaternary (Incuapa-Conicet) details how the specimens were revealed from the earth following a drought in the area that has sapped the stream, forcing the top of a shell into the open.
Farmer Juan de Dios Sota was taking his cows to graze when he spotted the unusual protrusion and didn’t recognize it to be the carcass of a horse or cow, which are common in the region. Upon spotting the shell, the farmer contacted the local authorities and a team of palaeontologists was sent out to recover the specimens and assess the four Glyptodons who it appears died together.
The unusual discovery will hopefully allow researchers to clarify if this species exhibited sexual dimorphism as the group is believed to be two adults and two juveniles of differing sexes. “These kind of cases, in which several individuals together who died in the same circumstances, are really exceptional and undoubtedly will give us a lot of information about these enigmatic animals and will allow us to test several hypotheses that we have been driving in recent years,” said palaeontologist on-site Ricardo Bonini, in a statement.
Regarding the sexual dimorphism, "It's not clear on how we are going to evaluate it in these fossils but the objective is to observe changes in the size of the bones because we have four glyptodonts together," Pablo Messineo, archaeologist, professor, and researcher at CONICET and INCUAPA, told IFLScience. "Maybe the bones of the pelvis and ventral shell can show some differences that we should study."
Glyptodons roamed in South America for more than 20 million years, and its thought they may have eventually gone extinct at the hands of early man, who may have used the shells of the dead animals as shelter during bad weather. These enormous, heavily armored relatives of armadillos are a part of the mammalian superorder Xenarthra. Like other Xenarthrans, they were herbivorous animals and as such their anatomy was adapted for protection.
They had immensely tough, tortoise-like shells that protected their body, and bony deposits on the skin called osteoderms to protect the parts that protruded from their armor. Despite being the size of modern cars, their arsenal of defense mechanisms implies they were preyed upon and their most likely assailant was a group known as the Terror Birds, a family of flightless carnivorous birds. Glyptodons were confirmed as relatives to modern-day armadillos, whose name in Spanish means “little armored one”, by DNA sequencing carried out in 2016.
Found a 70-million-year-old fossil of the largest fish that has ever existed in human history
Argentinean palaeontologists in Patagonia have found the remains of a massive carnivorous fish with razor sharp teeth. The species was "amongst the largest predatory fish that existed in the history of Earth."
A 70-million-year-old fossil of a 6-meter-long fish that lived among dinosaurs has been discovered in Argentina, a team of paleontologists said on 2020.
In Argentina's southern Patagonia region, researchers "found the remains of a predator fish that was more than six meters long," a carnivorous animal with sharp teeth and a "scary appearance."
The Argentinian paleontologists published their findings in the scientific journal Alcheringa: An Australasian Journal of Palaeontology.
The fossil belonged to the Xiphactinus genus, "amongst the largest predatory fish that existed in the history of Earth," according to the paleontologists.
They described the body of the fish as having been "notably slim" but that it ended in a massive head with large jaws and teeth "as sharp as needles, several centimeters long."
The giant fish "swam in the Patagonian seas at the end of the Cretaceous Period, when the temperature there was much more temperate than now," the study said.
'Preserved stomach contents'
The fossils of the giant fish were found nearby the Colhue Huapial lake, some 1,400 kilometers south of the capital Buenos Aires.
Julieta de Pasqua, one of the authors of the study, said examples of the Xiphactinus have also been discovered in other parts of the world, "some of which even have preserved stomach contents."
Previously, this species of fish had only been found in the northern hemisphere, with only one other example recently uncovered in Venezuela.
Patagonia is considered one of the greatest paleontological centers in the world. It is home to an important reservoir of dinosaur fossils, as well as fossils of other prehistoric sea and land species that are said to have ruled the area around 80 million years ago.
In February last year, paleontologists discovered fossils from a heretofore unknown species of dinosaur in Argentine Patagonia, estimated to have been about nine or 10 meters in length.
The "new" dinosaur belonged to the sauropod group and was notable for its large bony spikes covering its long neck and back. The dinosaur was labeled "Bajadasaurus pronuspinax," referring to the Bajada Colorada geological formation in Neuquen province, western Argentina, where the remains of the animal that lived approximately 140 million years ago were found.
Paleontologist Pablo Gallina described Bajadasaurus as a member of the dicraeosaurid family within the larger sauropod group.