In ancient Mesopotamia, the sky was not merely a backdrop to human life—it was a divine text. The movements of the sun, moon, planets, and stars were believed to reflect the intentions of the gods, offering guidance for every aspect of society. From kings and priests to farmers and temple workers, Mesopotamians looked to the heavens for signs that could shape religious rituals, political decisions, and agricultural planning.
As one of the earliest civilizations to systematically observe and record celestial phenomena, Mesopotamia laid the foundations of astrology as both a spiritual practice and an early scientific discipline.
Astrology and Mesopotamian Religion
Astrology was deeply woven into Mesopotamian religion. Celestial bodies were not seen as distant objects, but as manifestations of the gods themselves.
Key divine associations included:
Sin (Nanna): The moon god, associated with wisdom and time
Shamash (Utu): The sun god, linked to justice and truth
Ishtar (Inanna): The planet Venus, connected to love, war, and power
Marduk: Jupiter, symbolizing kingship and cosmic order
The sky functioned as a sacred language through which these gods communicated with humanity.
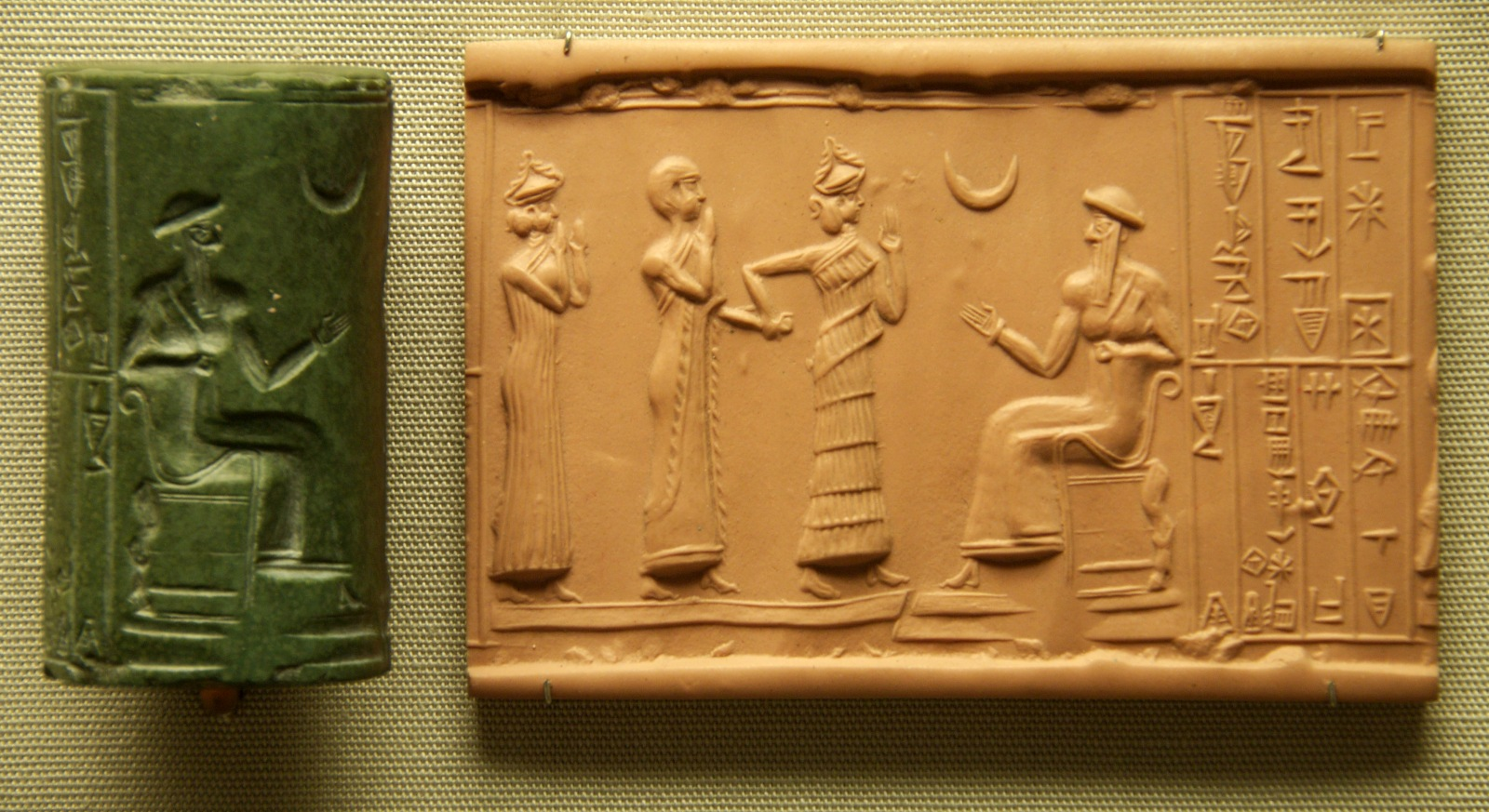
The Role of the Baru Priests
Astrological interpretation was carried out by priests known as baru. These specialists meticulously observed celestial events and consulted vast omen collections written in cuneiform.
One of the most famous astrological texts was the Enuma Anu Enlil, a massive series of tablets cataloging thousands of celestial omens. Each phenomenon—eclipses, planetary movements, unusual star patterns—was linked to specific predictions about political stability, natural disasters, or divine favor.
Political Power and Celestial Guidance
In Mesopotamia, ruling without divine approval was unthinkable. Kings depended heavily on astrologers to interpret the will of the gods before making major decisions.
Astrology influenced:
Military campaigns
Lawmaking
Temple construction
Succession planning
Nebuchadnezzar II and the Heavens
The Babylonian king Nebuchadnezzar II (r. 605–562 BCE) was particularly known for his reliance on celestial omens. Records show that astrologers monitored the skies to assess whether the gods supported his rule and military ambitions.
If an ominous sign appeared, rituals were performed to neutralize divine anger, including symbolic substitutions where a temporary “mock king” would absorb bad omens and be removed.
Astrology, therefore, was not symbolic—it was state policy.
Agriculture and the Cosmic Calendar
Mesopotamian farmers relied on the sky as a seasonal guide. The movements of the sun, moon, and stars helped determine:
When to plant crops
When to harvest
When floods might occur
When droughts were likely
The annual flooding of the Tigris and Euphrates rivers was essential for agriculture, and celestial observation allowed communities to anticipate these cycles.
By aligning farming practices with the heavens, Mesopotamians increased food security and strengthened the survival of their cities.
The Zodiac and Planetary Influence
Mesopotamia gave the world one of astrology’s most enduring structures: the twelve-sign zodiac.
Babylonian astronomers divided the sky into twelve equal sections, each associated with a constellation and later a zodiac sign. This system allowed them to track planetary movements with remarkable accuracy.
They believed that:
Planets represented divine forces
Their positions influenced human affairs
Specific signs carried symbolic meaning
This framework eventually passed into Greek, Roman, Islamic, and modern Western astrology.
Astrology as Early Science
Although astrology was religious in nature, it required precise observation, record-keeping, and prediction—hallmarks of early scientific thinking.
Mesopotamians:
Tracked lunar and solar eclipses
Recorded planetary cycles
Developed calendars
Created mathematical models of the heavens
Their work formed the basis of later astronomical traditions in Greece and the Islamic world.
Cultural and Spiritual Worldview
Astrology shaped how Mesopotamians understood reality itself. The universe was seen as an interconnected system where:
The gods ruled the heavens
Humans lived under divine influence
Natural events carried spiritual meaning
Every eclipse, comet, or planetary alignment was interpreted as a message requiring action, ritual, or reform.
This worldview reinforced social order, religious devotion, and obedience to divine authority.
The Lasting Legacy of Mesopotamian Astrology
The astrological systems developed in Mesopotamia did not disappear. They spread across civilizations:
Greek astrology adopted Babylonian zodiac systems
Roman culture integrated planetary symbolism
Islamic scholars refined astronomical models
Modern astrology still uses Mesopotamian foundations
Concepts such as zodiac signs, planetary influence, and cosmic cycles all trace back to the ancient cities of the Tigris and Euphrates.
Conclusion: A Civilization Guided by the Stars
For the people of Mesopotamia, the heavens were not distant—they were active participants in human destiny. Astrology shaped religion, politics, agriculture, and philosophy, providing a framework for understanding a complex and unpredictable world.
Through their systematic study of the sky, Mesopotamians transformed celestial observation into one of humanity’s earliest sciences. In doing so, they left behind a legacy that still influences how we interpret the cosmos today.
Sources & References
Encyclopaedia Britannica – Babylonian Astronomy
https://www.britannica.com/science/Babylonian-astronomyEncyclopaedia Britannica – Astrology
https://www.britannica.com/topic/astrologyBritish Museum – Mesopotamian Astrology Tablets
https://www.britishmuseum.orgNational Geographic – Ancient Astronomy
https://www.nationalgeographic.comRochberg, F. – The Heavenly Writing: Divination, Horoscopy, and Astronomy in Mesopotamian Culture
Cambridge University PressHunger & Pingree – Astral Sciences in Mesopotamia
Brill Academic Publishers