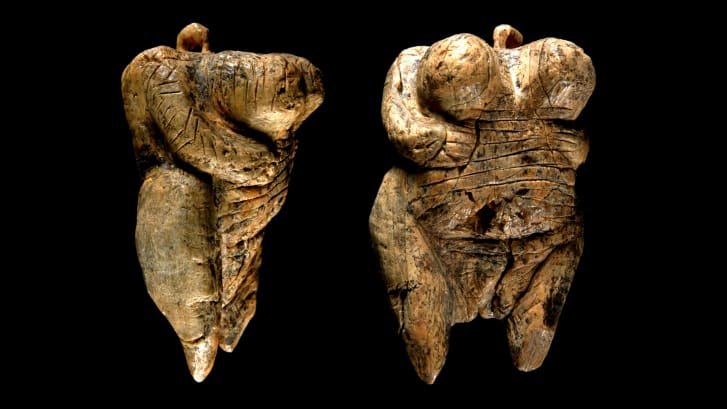
The Venus of Hohle Fels (also known as the Venus of Schelklingen; in German variously Venus vom Hohlen Fels, vom Hohle Fels; Venus von Schelklingen) is an Upper Paleolithic Venus figurine made of mammoth ivory that was unearthed in 2008 in Hohle Fels, a cave near Schelklingen, Germany. It is dated to between 40,000 and 35,000 years ago, belonging to the early Aurignacian, at the very beginning of the Upper Paleolithic, which is associated with the earliest presence of Cro-Magnon in Europe.
The figure is the oldest undisputed example of a depiction of a human being. In terms of figurative art only the lion-headed, zoomorphic Löwenmensch figurine is older. The Venus figurine is housed at the Prehistoric Museum of Blaubeuren (Urgeschichtliches Museum Blaubeuren).
Hohle Fels Cave, entrance. Photo: E. Sobkowiak.
The Swabian Alb region of Germany has a number of caves that have yielded many mammoth-ivory artifacts of the Upper Paleolithic period. Approximately 25 items have been discovered to date. These include the Löwenmensch figurine of Hohlenstein-Stadel dated to 40,000 years ago and an ivory flute found at Geißenklösterle, dated to 42,000 years ago. This mountainous region is located in Baden-Württemberg and is bounded by the Danube in the southeast, the upper Neckar in the northwest, and in the southwest it rises to the higher mountains of the Black Forest.
This concentration of evidence of full behavioral modernity, including figurative art and instrumental music among humans in the period of 40 to 30 thousand years ago, is unique worldwide and its discoverer, archaeologist Nicholas Conard, speculates that the bearers of the Aurignacian culture in the Swabian Alb may be credited with the invention, not just of figurative art and music, but possibly, the earliest religious practices as well. Within a distance of 70 cm to the Venus figurine, Conard's team also found a flute made from a vulture bone. Additional artifacts excavated from the same cave layer included flint-knapping debris, worked bone, and carved ivory as well as remains of tarpans, reindeer, cave bears, woolly mammoths, and Alpine Ibexes.
Interpretation
The discoverer, anthropologist Nicholas Conard, said: "This [figure] is about sex, reproduction... [it is] an extremely powerful depiction of the essence of being female".
Anthropologists from Victoria University of Wellington have suggested that such figurines were not depictions of beauty, but represented "hope for survival and longevity, within well-nourished and reproductively successful communities", reflecting the conventional interpretation of these types of figurines as representing a fertility goddess.