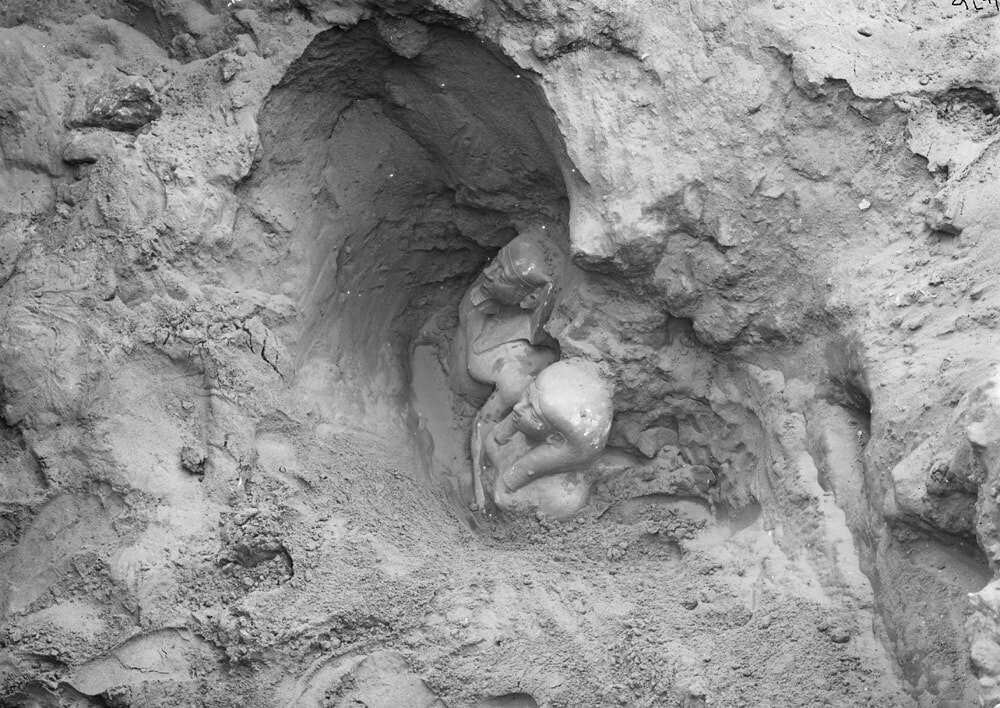
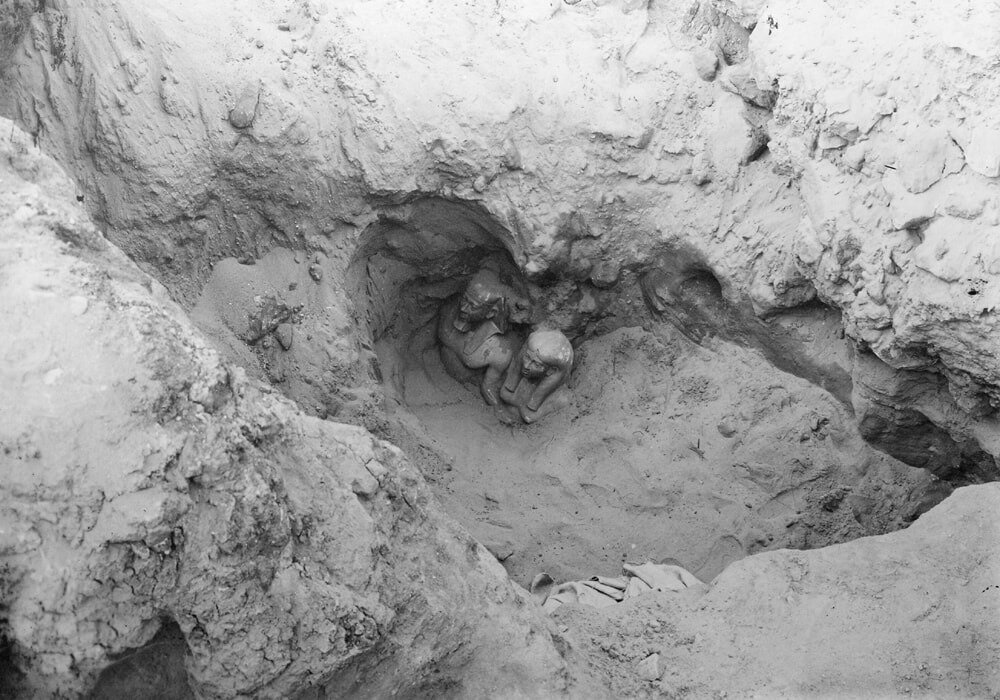
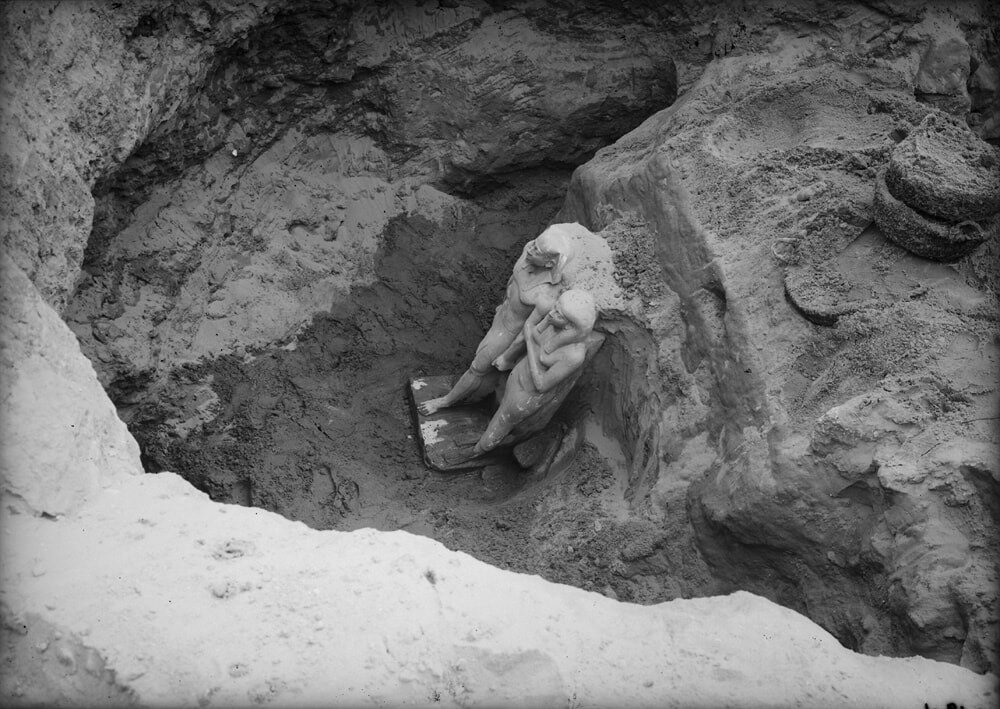
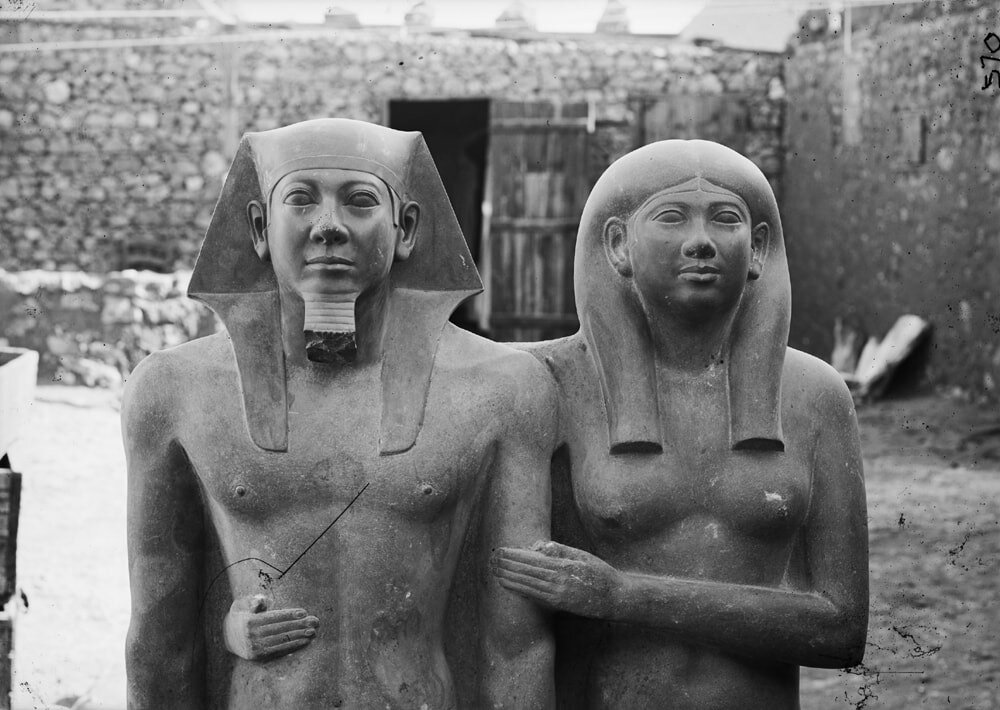
The moment of the great discovery of statue of King Menkaure (Mycerinus) and his wife Khamerernebty in the Temple of the King Menkaure Valley in Giza.
Serene ethereal beauty, raw royal power, and evidence of artistic virtuosity have rarely been simultaneously captured as well as in this breathtaking, nearly life-size statue of the pharaoh Menkaure and a queen. Smooth as silk, the meticulously finished surface of the dark stone captures the physical ideals of the time and creates a sense of eternity and immortality even today.
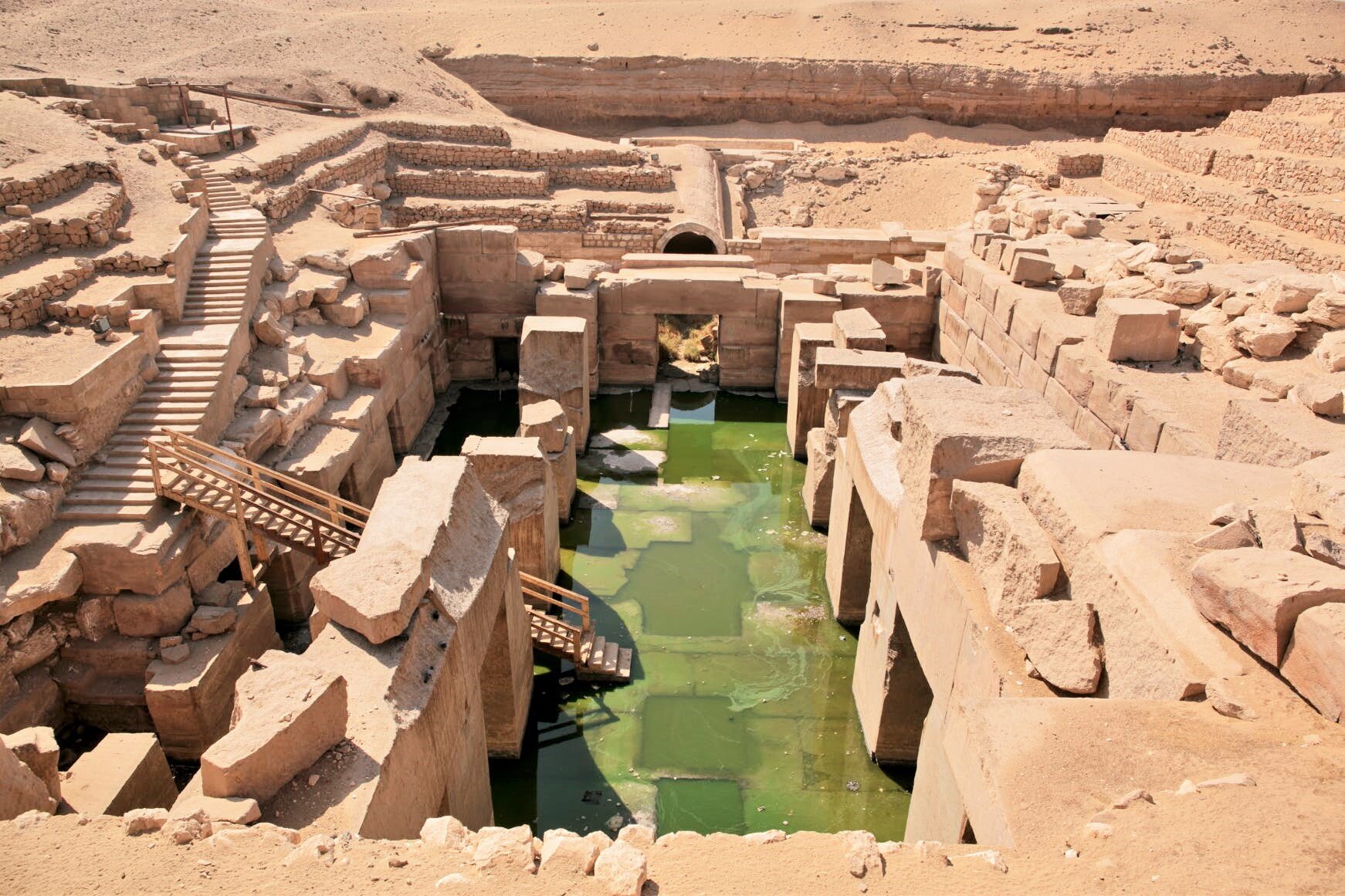
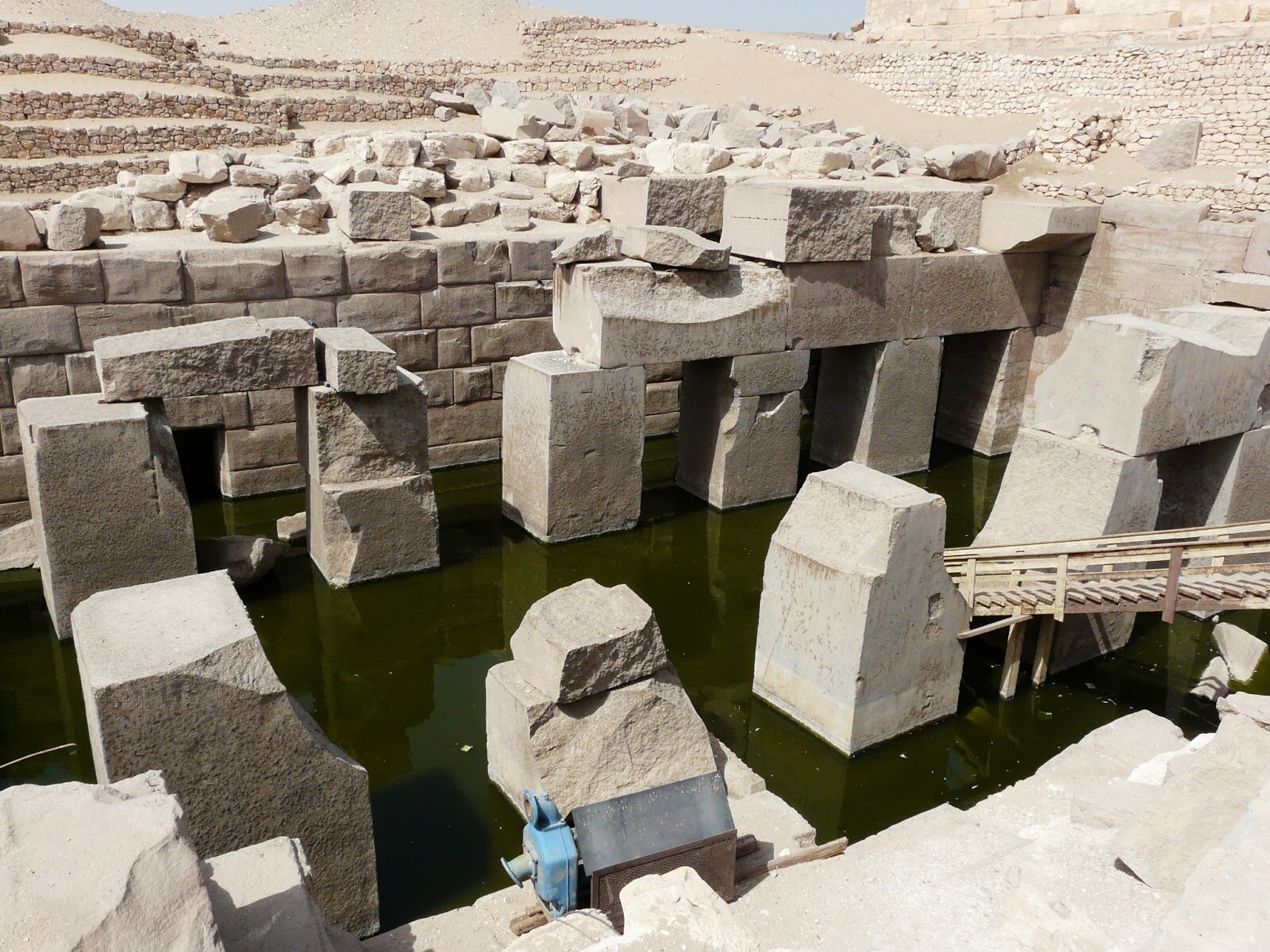
Pyramids are not stand-alone structures. Those at Giza formed only a part of a much larger complex that included a temple at the base of the pyramid itself, long causeways and corridors, small subsidiary pyramids, and a second temple (known as a valley temple) some distance from the pyramid. These Valley Temples were used to perpetuate the cult of the deceased king and were active places of worship for hundreds of years (sometimes much longer) after the king’s death. Images of the king were placed in these temples to serve as a focus for worship—several such images have been found in these contexts, including the magnificent seated statue of Khafre, now in the Egyptian Museum in Cairo.
Menkaure's Pyramid Complex.
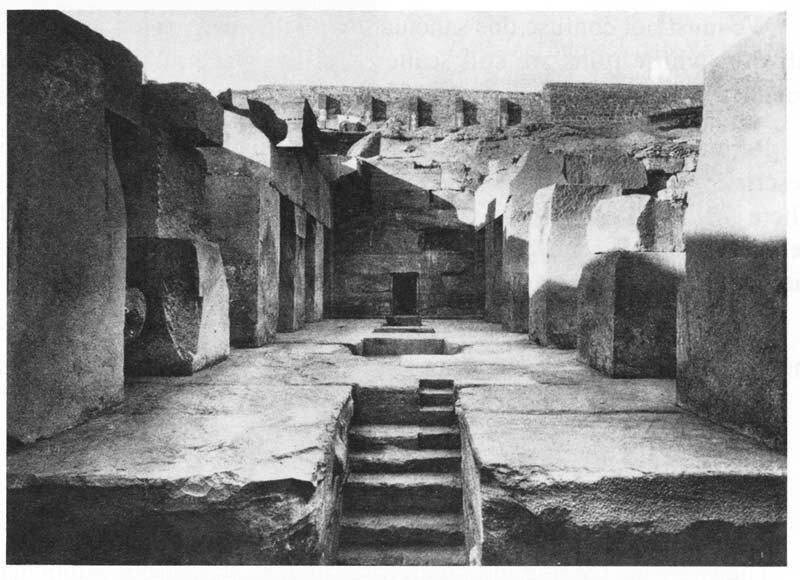
On January 10, 1910, excavators under the direction of George Reisner, head of the joint Harvard University-Museum of Fine Arts, Boston, Expedition to Egypt, uncovered an astonishing collection of statuary in the Valley Temple connected to the Pyramid of Menkaure. Menkaure’s pyramid had been explored in the 1830s (using dynamite, no less). His carved granite sarcophagus was removed (and subsequently lost at sea), and while the Pyramid Temple at the base was in only mediocre condition; the Valley Temple, was—happily—basically ignored.
Reisner had been excavating on the Giza plateau for several years at this point; his team had already explored the elite cemetery to the west of the Great Pyramid of Khufu before turning their attention to the Menkaure complex, most particularly the barely-touched Valley Temple.
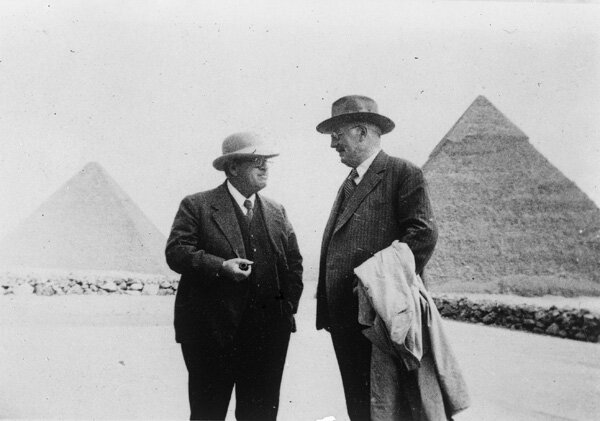
George Reisner and Georg Steindorff at Harvard Camp, looking east toward Khufu and Khafre pyramids, 1935, photo by Albert Morton Lythgoe.
In the southwest corner of the structure, the team discovered a magnificent cache of statuary carved in a smooth-grained dark stone called greywacke or schist. There were a number of triad statues—each showing 3 figures—the king, the fundamentally important goddess Hathor, and the personification of a nome (a geographic designation, similar to the modern idea of a region, district, or county). Hathor was worshipped in the pyramid temple complexes along with the supreme sun god Re and the god Horus, who was represented by the living king. The goddess’s name is actually ‘Hwt-hor’, which means “The House of Horus,” and she was connected to the wife of the living king and the mother of the future king. Hathor was also a fierce protector who guarded her father Re; as an "Eye of Re" (the title assigned to a group of dangerous goddesses), she could embody the intense heat of the sun and use that blazing fire to destroy his enemies.
There were 4 complete triads, one incomplete, and at least one other in a fragmentary condition. The precise meaning of these triads is uncertain. Reisner believed that there was one for each ancient Egyptian nome, meaning there would have originally been more than thirty of them. More recent scholarship, however, suggests that there were originally 8 triads, each connected with a major site associated with the cult of Hathor. Hathor’s prominence in the triads (she actually takes the central position in one of the sculptures) and her singular importance to kingship lends weight to this theory.
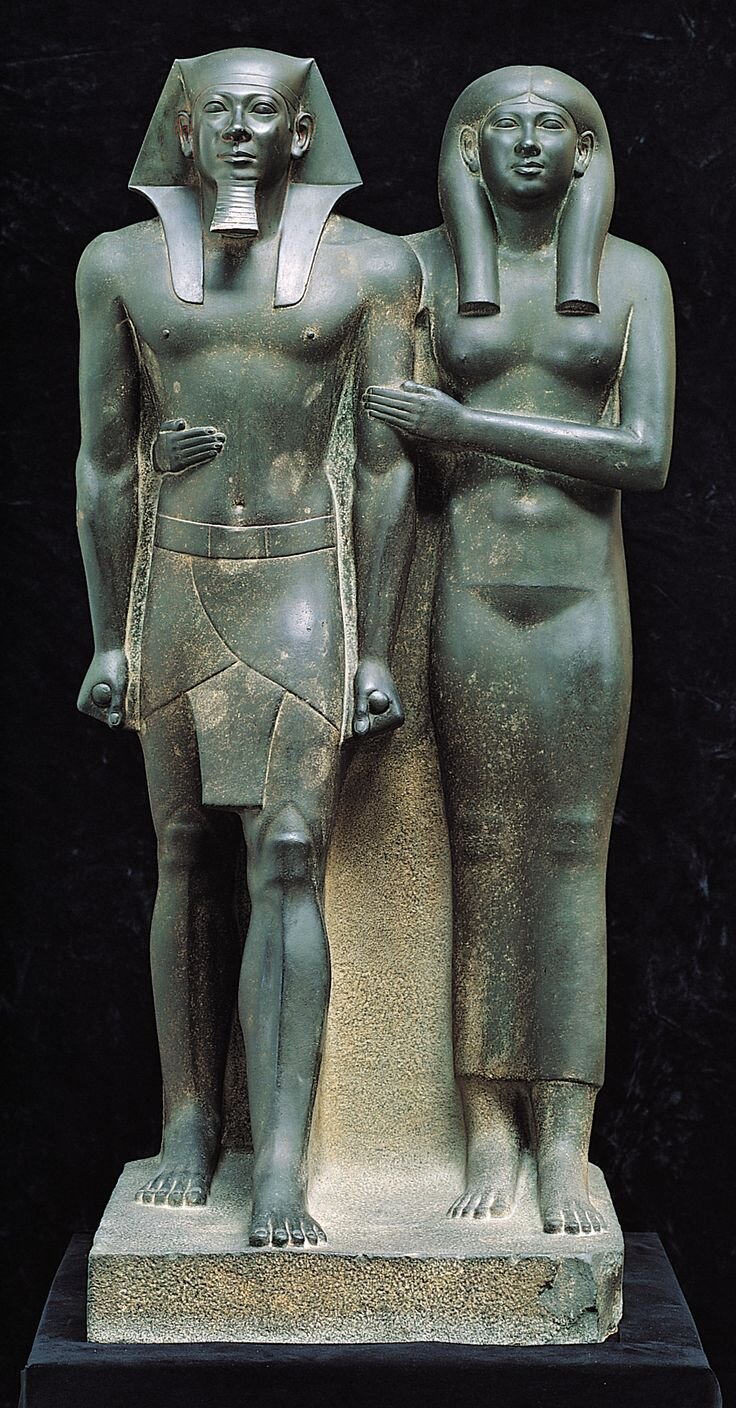
In addition to the triads, Reisner’s team also revealed the extraordinary dyad statue of Menkaure and a queen that is breathtakingly singular.
The two figures stand side-by-side on a simple, squared base and are supported by a shared back pillar. They both face to the front, although Menkaure’s head is noticeably turned to his right—this image was likely originally positioned within an architectural niche, making it appear as though they were emerging from the structure. The broad-shouldered, youthful body of the king is covered only with a traditional short pleated kilt, known as a shendjet, and his head sports the primary pharaonic insignia of the iconic striped nemes headdress (so well known from the mask of Tutankhamun) and an artificial royal beard. In his clenched fists, held straight down at his sides, Menkaure grasps ritual cloth rolls. His body is straight, strong, and eternally youthful with no signs of age. His facial features are remarkably individualized with prominent eyes, a fleshy nose, rounded cheeks, and full mouth with protruding lower lip.
Menkaure’s queen provides the perfect female counterpart to his youthful masculine virility. Sensuously modelled with a beautifully proportioned body emphasized by a clinging garment, she articulates ideal mature feminine beauty. There is a sense of the individual in both faces. Neither Menkaure nor his queen are depicted in the purely idealized manner that was the norm for royal images. Instead, through the overlay of royal formality we see the depiction of a living person filling the role of pharaoh and the personal features of a particular individual in the representation of his queen.
Menkaure and his queen stride forward with their left feet—this is entirely expected for the king, as males in Egyptian sculpture almost always do so, but it is unusual for the female since they are generally depicted with feet together. They both look beyond the present and into timeless eternity, their otherworldly visage displaying no human emotion whatsoever.
The dyad was never finished—the area around the lower legs has not received a final polish, and there is no inscription. However, despite this incomplete state, the image was erected in the temple and was brightly painted—there are traces of red around the king’s ears and mouth and yellow on the queen’s face. The presence of paint atop the smooth, dark greywacke on a statue of the deceased king that was originally erected in his memorial temple courtyard brings an interesting suggestion—that the paint may have been intended to wear away through exposure and, over time, reveal the immortal, black-fleshed
"Osiris" Menkaure.
Unusual for a pharaoh’s image, the king has no protective cobra (known as a uraeus) perched on his brow. This notable absence has led to the suggestion that both the king’s nemes and the queen’s wig were originally covered in precious metal and that the cobra would have been part of that addition.
Based on comparison with other images, there is no doubt that this sculpture shows Menkaure, but the identity of the queen is a different matter. She is clearly a royal female. She stands at nearly equal height with the king and, of the two of them, she is the one who is entirely frontal. In fact, it may be that this dyad is focused on the queen as its central figure rather than Menkaure. The prominence of the royal female—at equal height and frontal—in addition to the protective gesture she extends has suggested that, rather than one of Mekaure’s wives, this is actually his queen-mother. The function of the sculpture in any case was to ensure rebirth for the king in the Afterlife.
Essay by Dr. Amy Calvert