EILSLEBEN, GERMANY — According to Live Science, excavations at an early farming settlement near Eilsleben in northern Germany have revealed new insights into contact between local hunter-gatherers and some of Europe’s first farmers.
Archaeologists think the site functioned as a frontier settlement for early Neolithic farmers who migrated from Anatolia into central Europe around 5375 B.C. and established the village. Recent digs have uncovered houses, graves, pits, and artifacts linked to the Linear Pottery culture (LBK), one of the earliest farming cultures in the region.
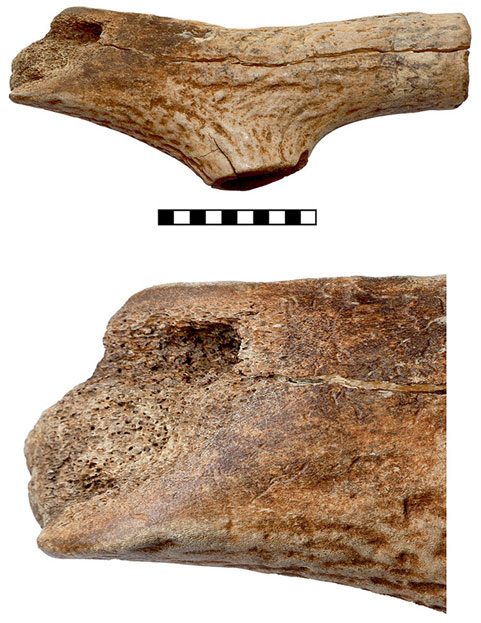
Unexpectedly, researchers also discovered clearly Mesolithic items, including a deer skull headdress similar to those found at hunter-gatherer sites across Europe. In addition, they unearthed antler tools—materials not typically associated with LBK farming communities.
Laura Dietrich of Martin Luther University Halle-Wittenberg noted that finding both Mesolithic and Neolithic objects together at one location is unusual. She proposes that the settlement may have been a meeting point where incoming farmers and indigenous hunter-gatherers interacted, sharing goods, knowledge, and technologies.
The full study appears in the journal Antiquity.